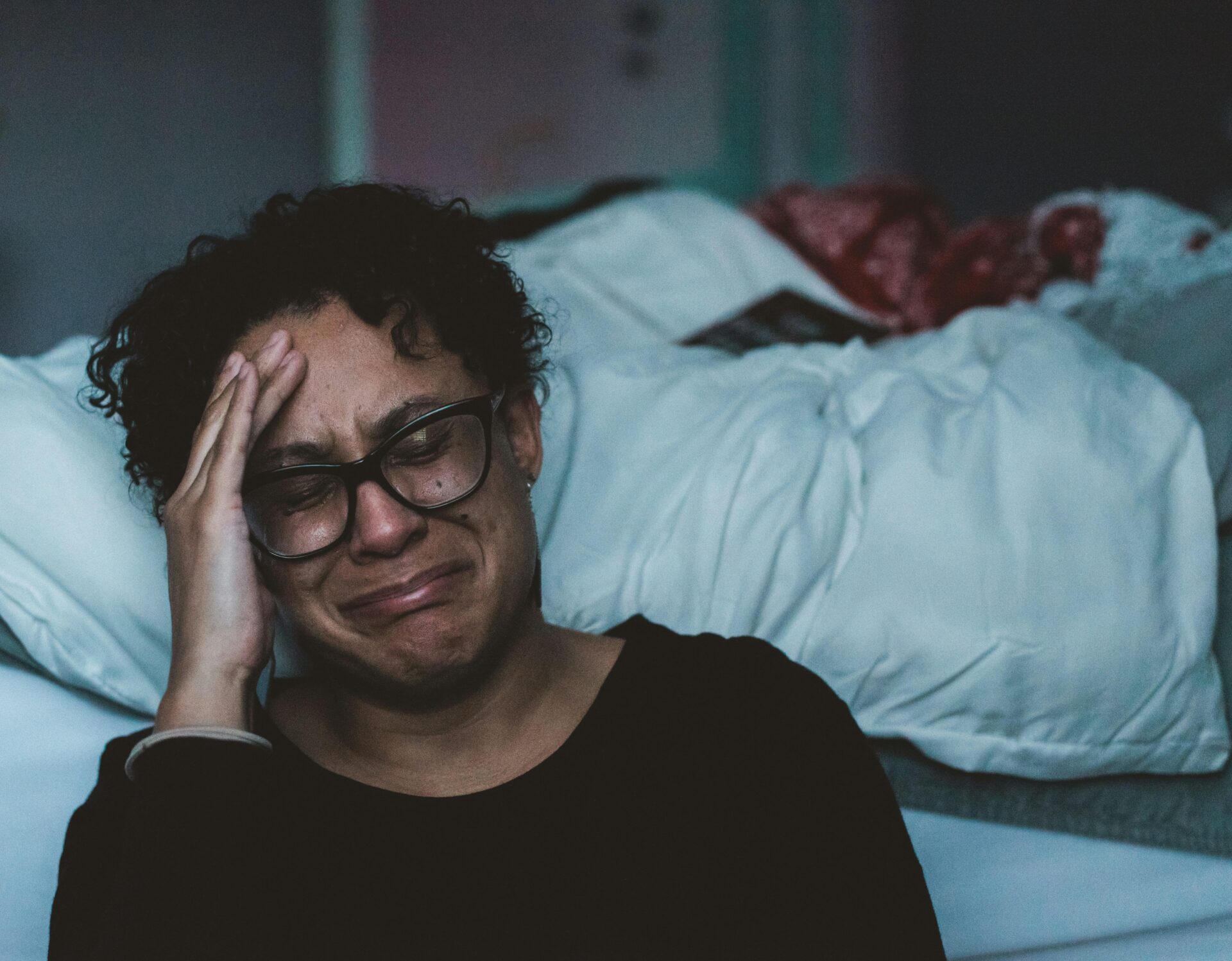
Understanding Triggers
Triggers are specific events, situations, or experiences that provoke a strong emotional or psychological response. They can cause you to relive past traumas, evoke intense feelings, or prompt automatic reactions that disrupt your emotional stability. Understanding triggers is essential for managing them effectively and maintaining mental well-being.
There are various types of triggers, including:
- Emotional Triggers: Events or situations that evoke strong emotional responses, such as anger, sadness, or anxiety.
- Environmental Triggers: Aspects of your surroundings, like clutter, noise, or certain locations, that can trigger discomfort or stress.
- Relational Triggers: Interactions with others that provoke negative emotions or stress, such as conflict or criticism.
- Physical Triggers: Physical sensations or health issues that can lead to emotional responses, such as pain or fatigue.
Understanding how triggers affect you involves recognizing both the immediate and lingering impacts. When you’re triggered, you might experience a range of responses, including heightened stress, anxiety, or even a return to past traumatic experiences. These reactions can influence your mood, behavior, and overall quality of life.
By identifying and understanding your triggers, you can begin to develop strategies to manage your reactions and improve your emotional resilience. In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into recognizing your personal triggers and practical ways to handle them effectively.
Recognizing Your Triggers
Recognizing your triggers is a crucial step in managing them effectively. Understanding what specifically sets off your emotional or psychological responses can help you prepare and respond in a healthier way. Let’s explore some methods to identify these triggers and the signs that they are affecting you.
Self-Observation Techniques: One of the most effective ways to identify your triggers is through self-observation. Keeping a journal can be incredibly helpful in this process. Note down moments when you experience strong emotional reactions, and detail the circumstances surrounding these moments. Over time, patterns may emerge that highlight specific triggers.
Identifying Patterns: As you track your emotional responses, look for recurring themes. Do you find that certain situations, environments, or interactions consistently lead to heightened stress or discomfort? Identifying these patterns can help you pinpoint specific triggers and understand how they affect you.
Common Signs of Being Triggered: Recognizing when you’re triggered involves paying attention to both physical and emotional signs. You might experience physical symptoms like a racing heart, sweating, or muscle tension. Emotionally, you may feel sudden waves of anger, sadness, or anxiety. Behavioral signs include withdrawing from situations or reacting more intensely than usual.
Examples of How Triggers Manifest: Triggers can manifest in various ways. For example, a particular smell might remind you of a stressful event, or a specific type of feedback at work could trigger feelings of inadequacy. Understanding these manifestations helps you prepare and respond more effectively when faced with similar situations.
By becoming more aware of your triggers and how they affect you, you’re better equipped to manage your reactions and develop strategies to cope. In the next section, we’ll delve into how to identify your personal triggers and explore methods to better understand what might be influencing your emotional responses.
Identifying Your Personal Triggers
Identifying your personal triggers involves a deeper exploration of your experiences and emotions. This process can help you uncover the specific factors that influence your emotional responses and contribute to stress or discomfort. Here’s how you can go about pinpointing these triggers effectively.
Reflect on Past Experiences: Take some time to review past events that have led to strong emotional reactions. Think about situations or interactions that have left you feeling particularly stressed, upset, or overwhelmed. Reflecting on these experiences can provide clues about what might be triggering these responses. Consider how these events have impacted you and what common elements they share.
Analyze Relationships and Environments: Pay attention to the people and places that consistently evoke strong feelings. Are there certain relationships or environments that seem to trigger negative emotions more than others? For example, conflicts with a specific person or being in a particular setting might be common triggers. Understanding these dynamics can help you identify specific relational or environmental triggers.
Engage in Self-Reflection: Self-reflection is key to uncovering your personal triggers. Use techniques such as mindfulness or meditation to explore your emotional responses more deeply. Ask yourself questions like: “What situations cause me to feel anxious or frustrated?” or “When do I notice my mood shifting significantly?” These reflections can reveal underlying triggers and provide insight into how they affect you.
Questions to Ask Yourself: To aid in this process, consider the following questions:
- What recent events have caused me significant emotional reactions?
- Are there specific people or situations that consistently trigger my stress or discomfort?
- What physical or emotional symptoms do I experience when I’m triggered?
- How do I usually respond when I’m faced with these triggers?
By exploring these questions and reflecting on your experiences, you can gain a clearer understanding of your personal triggers. This awareness is the first step in developing effective strategies to manage and mitigate their impact. In the following sections, we’ll discuss practical ways to manage these triggers and create a plan for handling them effectively.
Managing Your Triggers
Once you’ve identified your personal triggers, the next step is to develop strategies to manage them effectively. Managing your triggers involves both immediate coping techniques and long-term strategies to minimize their impact on your life. Let’s explore some practical methods for handling triggers and maintaining emotional stability.
Develop Coping Strategies: Immediate coping strategies are essential for managing your reactions when you encounter a trigger. Techniques such as deep breathing, grounding exercises, or mindfulness can help you stay calm and centered. For example, when you feel triggered, try taking slow, deep breaths to calm your nervous system, or use grounding techniques like focusing on the present moment to regain control.
Long-Term Strategies: In addition to immediate coping techniques, developing long-term strategies can help you address triggers more effectively. Cognitive restructuring, which involves challenging and changing negative thought patterns, can be helpful. Emotional regulation techniques, such as practicing self-compassion and developing resilience, can also contribute to long-term emotional stability.
Creating a Trigger Management Plan: Developing a personalized trigger management plan can provide a structured approach to handling triggers. Start by listing your known triggers and the specific emotional or physical responses they provoke. Then, outline your coping strategies for each trigger. This plan should be flexible and adaptable, allowing you to make adjustments as needed based on your experiences and evolving needs.
Importance of Flexibility: It’s important to recognize that managing triggers is an ongoing process. Your triggers and responses might change over time, so your management plan should be flexible. Regularly review and update your strategies to ensure they remain effective. Adaptability is key to successfully managing triggers and maintaining your emotional well-being.
By implementing both immediate and long-term strategies, you can effectively manage your triggers and improve your overall emotional resilience. In the next sections, we’ll explore preventive measures to minimize exposure to triggers and discuss the role of professional support in managing your emotional health.
Implementing Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are a proactive way to manage triggers and minimize their impact before they become overwhelming. By making adjustments to your environment and relationships, and by incorporating self-care practices into your routine, you can reduce the likelihood of being triggered and enhance your overall emotional resilience.
Environmental Adjustments: One effective way to prevent triggers is to modify your surroundings to reduce exposure to known stressors. This could involve decluttering your workspace, creating a calming environment at home, or avoiding specific locations or situations that have previously triggered you. For example, if a noisy environment increases your stress, consider using noise-canceling headphones or finding a quieter place to work.
Building Healthy Relationships: Your relationships can significantly influence your emotional well-being. Establishing clear boundaries and practicing effective communication can help manage relational triggers. For instance, if certain interactions with people tend to provoke strong reactions, discuss your needs and boundaries openly to create a more supportive and understanding dynamic.
Self-Care Practices: Regular self-care is crucial for maintaining emotional balance and resilience. Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies you enjoy. Creating a self-care routine that includes activities that help you unwind and recharge can make you more resilient to potential triggers.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Beyond immediate coping strategies, developing healthy habits for managing stress can also be beneficial. This might include practices like journaling, engaging in physical activity, or seeking support from friends or support groups. Having a toolkit of positive coping mechanisms can help you navigate triggers more effectively.
By proactively implementing these preventive measures, you can create a more supportive environment and build resilience against potential triggers. In the following sections, we’ll discuss when and how to seek professional support for additional help in managing your emotional health and creating a comprehensive trigger management plan.
Seeking Professional Support
When managing triggers becomes overwhelming, seeking professional support can provide valuable assistance. Mental health professionals are trained to help you understand and address the underlying issues contributing to your emotional responses. Here’s when and how to seek help, and what to expect from professional support.
When to Seek Help: If you find that your triggers are significantly impacting your daily life, relationships, or overall well-being, it may be time to seek professional support. Signs that you might benefit from therapy include persistent feelings of stress, difficulty managing emotional responses, or a sense that your current coping strategies are not effective.
Types of Professionals: Various types of mental health professionals can help you manage triggers and improve your emotional health. These include:
- Therapists: Licensed therapists, such as clinical psychologists or licensed professional counselors, provide talk therapy to explore and address emotional and psychological issues.
- Counselors: Professional counselors offer guidance and support in managing stress and emotional difficulties, often focusing on specific areas like relationships or career challenges.
- Psychiatrists: Psychiatrists are medical doctors who can prescribe medication and provide therapy for more severe mental health conditions.
- Social Workers: Clinical social workers offer therapy and support, often with a focus on improving overall functioning and access to resources.
How Therapy Can Help: Therapy can provide a structured and supportive environment to explore your triggers and develop effective coping strategies. A mental health professional can help you:
- Identify and understand your triggers more deeply.
- Develop personalized strategies for managing and responding to triggers.
- Work through underlying issues contributing to your emotional responses.
- Build resilience and improve overall emotional well-being.
Finding the Right Professional: It’s important to find a mental health professional who is a good fit for your needs. Consider factors such as their area of expertise, approach to therapy, and whether you feel comfortable working with them. Don’t hesitate to reach out for initial consultations or ask for recommendations to find the right support.
Seeking professional support can be a powerful step in managing your triggers and enhancing your emotional health. With the right help, you can gain new insights, develop effective strategies, and achieve greater stability and well-being. In the next section, we’ll discuss how to monitor and adjust your strategies over time to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Strategies
Managing triggers is an ongoing process, and it’s important to regularly monitor and adjust your strategies to ensure they remain effective. As you navigate through different phases of life, your triggers and responses may evolve, so keeping track of your progress and making necessary adjustments is crucial for maintaining emotional stability.
Ongoing Self-Assessment: Regularly evaluate how well your current strategies are working. This can be done through self-reflection, journaling, or even discussing your experiences with a mental health professional. Ask yourself questions such as:
- Are my current coping strategies still effective in managing my triggers?
- Have I noticed any new triggers or changes in my emotional responses?
- What adjustments can I make to improve my trigger management?
Keeping track of your progress helps you stay aware of what works and what doesn’t, allowing you to refine your approach over time.
Adapting Your Plan: Based on your ongoing self-assessment, be prepared to make adjustments to your trigger management plan. This might involve updating your coping strategies, trying new techniques, or modifying your environment or routines. Flexibility is key to effectively managing triggers as your needs and circumstances change.
Responding to Changes: Life circumstances and emotional responses can shift, so it’s important to remain adaptable. If you encounter new triggers or notice changes in how you’re affected, update your strategies accordingly. For example, if a previously manageable situation becomes more challenging, reassess your coping mechanisms and make necessary changes to your plan.
Seeking Feedback: Don’t hesitate to seek feedback from trusted friends, family, or a mental health professional. They can offer valuable perspectives on your progress and suggest additional strategies or adjustments. Collaboration can enhance your approach to managing triggers and provide additional support.
Monitoring and adjusting your strategies ensures that you remain proactive in managing your triggers and maintaining your emotional well-being. By staying vigilant and flexible, you can better navigate the complexities of trigger management and continue to make positive strides toward emotional stability. In the next section, we’ll explore real-life examples and case studies to illustrate how others have successfully managed their triggers.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Understanding how others have successfully managed their triggers can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your own journey. Real-life examples and case studies highlight practical strategies and personal experiences that demonstrate effective trigger management. Let’s explore a few stories and lessons learned from individuals who have navigated their triggers successfully.
Personal Stories: Real-life stories can offer practical examples of how people have identified and managed their triggers. For instance, consider Sarah, who struggled with workplace stress triggered by frequent deadlines. By recognizing this pattern, she implemented a structured work schedule, prioritized self-care, and learned relaxation techniques. Over time, these changes helped her manage her stress more effectively and improve her overall well-being.
Case Study 1: John experienced significant anxiety in social situations, particularly during networking events. Through therapy, he identified that his anxiety was linked to past experiences of rejection. By working with his therapist, John developed coping strategies such as cognitive restructuring and gradual exposure to social settings. His proactive approach led to improved confidence and reduced anxiety in social situations.
Case Study 2: Lisa found that her triggers were often related to conflicts in personal relationships. After recognizing these triggers, she focused on improving her communication skills and setting clear boundaries with her loved ones. By addressing these issues directly and practicing assertiveness, Lisa managed to reduce the frequency and intensity of her emotional reactions, leading to healthier relationships and better emotional balance.
Lessons Learned: From these examples, several key lessons emerge:
- Self-Awareness is Crucial: Understanding your triggers and their impact is the first step in managing them effectively.
- Effective Strategies Require Adaptation: What works for one person might need to be adjusted for another. Tailoring strategies to your unique needs is important.
- Professional Support Can Be Beneficial: Therapy and counseling provide valuable tools and insights for managing triggers and improving emotional health.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and adjusting your strategies helps ensure ongoing effectiveness and personal growth.
Real-life examples and case studies offer practical insights and inspiration for managing triggers. By learning from others’ experiences and applying these lessons to your own life, you can enhance your approach to trigger management and work towards achieving greater emotional stability and well-being. In the next section, we’ll provide resources and tools to support you in your journey.
Resources and Tools for Managing Triggers
Having the right resources and tools can significantly enhance your ability to manage triggers and maintain emotional well-being. Whether you’re looking for practical tools to help you cope with immediate stress or seeking additional support for long-term management, there are various resources available to assist you. Let’s explore some of these resources and tools that can aid in your journey.
Self-Help Books: There are many self-help books that offer valuable insights and strategies for managing triggers. Books on emotional resilience, stress management, and cognitive-behavioral techniques can provide practical advice and exercises to help you understand and address your triggers. Some recommended titles include:
- The Anxiety and Phobia Workbook by Edmund J. Bourne
- Feeling Good: The New Mood Therapy by David D. Burns
- Mindfulness for Beginners by Jon Kabat-Zinn
Mobile Apps: Several mobile apps can support your trigger management efforts by offering tools for relaxation, mindfulness, and emotional tracking. Popular apps include:
- Headspace: Offers guided meditation and mindfulness exercises.
- Calm: Provides relaxation techniques, sleep aids, and stress management resources.
- MyTherapy: Helps you track your mood and medication, with reminders and reports to discuss with your therapist.
Online Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences can be beneficial. Online support groups and forums offer a platform for discussing challenges, sharing strategies, and receiving encouragement. Consider exploring platforms like:
- Reddit’s r/depression: A community where individuals discuss their experiences and coping strategies.
- 7 Cups: Provides anonymous emotional support and connects users with trained listeners and therapists.
- Support groups on Facebook: Various groups focus on mental health topics and provide a space for sharing and support.
Professional Resources: In addition to self-help tools, professional resources such as therapy directories and mental health organizations can help you find qualified professionals and additional support. Consider using resources like:
- Psychology Today: Offers a directory of therapists and counselors, with filters to find specialists who match your needs.
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI): Provides information on mental health conditions, support resources, and local support groups.
- BetterHelp: An online platform offering virtual counseling and therapy services.
Utilizing these resources and tools can enhance your ability to manage triggers and improve your emotional resilience. By exploring these options and integrating them into your daily routine, you can better navigate the challenges of trigger management and support your overall well-being. In the final section, we’ll summarize the key points and offer some closing thoughts on the journey of managing triggers.
Managing triggers is a vital part of maintaining emotional well-being and leading a balanced life. By understanding and identifying your triggers, implementing effective management strategies, and utilizing available resources, you can navigate life’s challenges with greater resilience and stability. Let’s recap the key points and offer some final thoughts on your journey.
Key Takeaways:
- Identifying Triggers: Recognize and understand what triggers strong emotional responses in your life. This awareness is the first step towards effective management.
- Managing Triggers: Develop and apply both immediate and long-term strategies to cope with triggers. Adapt these strategies as needed to suit your evolving needs and circumstances.
- Preventive Measures: Implement changes in your environment, relationships, and self-care practices to reduce exposure to known triggers and enhance your overall well-being.
- Professional Support: Seek help from mental health professionals when needed. They can offer valuable insights, tools, and support to manage triggers effectively.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your strategies and make adjustments as necessary. Flexibility and ongoing self-reflection are key to maintaining effective trigger management.
- Resources and Tools: Utilize self-help books, mobile apps, online support groups, and professional resources to support your trigger management efforts and enhance your emotional resilience.
Final Thoughts: Managing triggers is an ongoing journey that requires patience, self-awareness, and a proactive approach. Remember that it’s okay to seek help and use available resources to support you along the way. Everyone’s experience with triggers is unique, so finding what works best for you is an essential part of the process. Stay committed to your well-being and continue to explore and refine your strategies as you grow.
By applying these principles and strategies, you can better understand and manage your triggers, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling life. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical tools to support your emotional health journey. Remember, you’re not alone in this process, and there’s always support available when you need it.